 |
 |
 |
 |
| Wordfast Server user manual |
| 13 | The Setup tab | |
|---|---|---|
The Setup tab sets up many WFS options. They are:

Organizations with more than 3 employees, such as corporations, translation agencies, or institutions, must have a valid license to run WFS in production mode. Without a valid license number, WFS runs in demo mode, which is only allowed for evaluation purposes, or for production use by individual (“freelance”) translators working as self-employed individuals. In the demo mode, WFS does not serve more than three “clients” simultaneously. That is the only limitation. When you enter a license number in the red textbox, the textbox background turns to white if the license number is correct, and WFS runs in production mode.
Check the System cache checkbox to boost hard disk operation performance on regular Windows versions. On Windows server versions, the system cache is enabled by default, so it is not necessary to check that option.
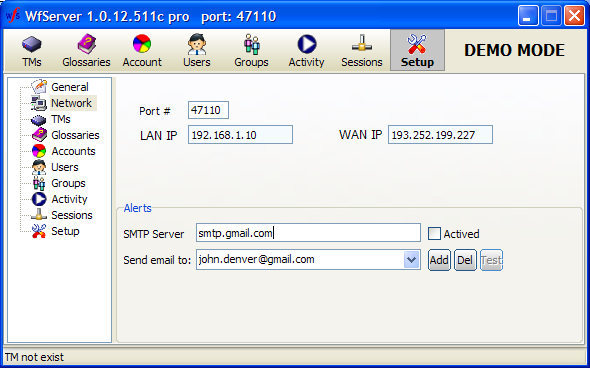
By default, WFS uses port 47110 for communication. We advise using that port. The Wordfast client is set to use port 47110 by default, in the absence of a specified port. Port 47110 is not a standard Windows port, and is less likely to be bombarded by hostile pings and pressure. You can use another port number, but then, clients that access WFS must specify the same port number right after the server’s IP number in their connection string, as in the following example, where port 500 is forced:
john:mypass@domain.com:500 or
john:mypass@167.67.78.1:500
If 47110 is used, clients only need to specify:
john:mypass@domain.com or
john:mypass@167.67.78.1
The WFS administrator can specify an email address (and the relevant SMTP server for mail relay) to receive automatic notifications. Notifications are critical events registered by the server, such as starting up, closing down, or faults.
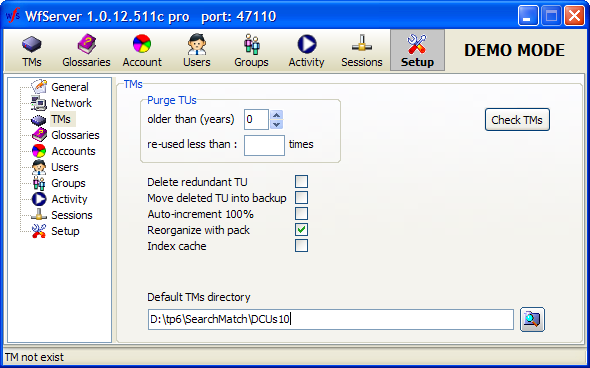
The server can automatically delete TUs if:
They are older than X years
They were re-used less than X times.
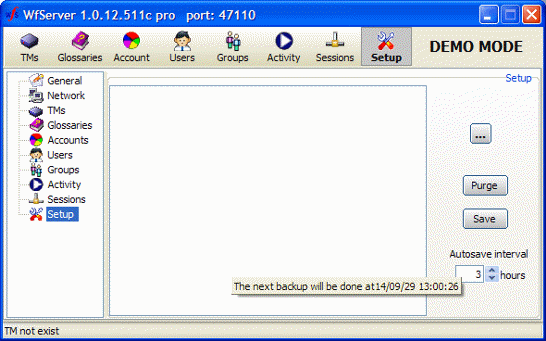
Values 1. and 2. are entered in the TMs section of the Setup tab. Actual purge is done by right-clicking a TM in the list of TMs in the TM tab, and choosing the Purge option.
Check the Delete redundant TUs checkbox if WFS must delete existing redundant TUs when TUs are being added to the server. Redundant TUs are defined as TUs where source segments are identical. If a different definition of a TU must be used (for instance, redundant TUs are those where both source and target segments are identical, or where the degree of matching is above 95%; or where attributes are identical too), the translation client should make the decision.
Check the Auto-increment 100% checkbox if WFS must increment a TU’s "Re-use" counter if it serves a 100% match originating from that TU.
Check the Reorganize with pack checkbox if WFS must pack holes during reorganization. When a TU is deleted, it is filled with whitespace, creating a “hole” in the database. The holes are often reused in real time when TUs are added, but sometimes some holes cannot be reused. That is why it is necessary to remove the holes during the reorganization.
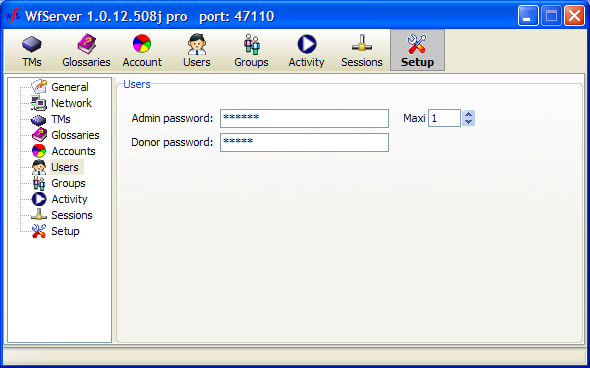
The Admin password can be set here. It is required by any “client” that wishes to connect to the server in Admin (administrator) mode. At this time, no application exists to pilot WFS from a remote location in administration mode, but the API explains how such a client application can connect to WFS in admin mode.
We recommend accessing WFS in remote desktop mode to set it up or administer it by directly manipulating its user interface.
The Maxi value is the maximum number of persons that can simultaneously access the server in Admin mode.
The Donor password is “Donor” by default. It allows clients accessing the server in “Donor” mode to write public TUs into a TM. “Public Tus” are visible to anyone accessing the server, so they are considered as being “donated” to the public. Public does not mean “the public” at large. Public distinguishes these TUs from private TUs in the same TM. Private TUs have a WorkGroupID attached to them and are only visible to clients using the same WorkGroupID.
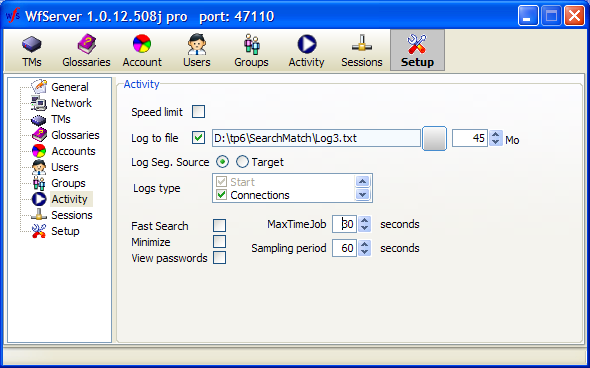
Speed limit: If checked, WFS’ overall speed is limited to a certain number of requests per second.
Log to file: This setting lets the administrator specify whether the activity log is written to a log file.
Minimize: Specifies whether WFS minimizes itself in the system tray after a while.
MaxTimeJob: This threshold limits the time spent on typical production short jobs, such as search, concordance, TU writes, etc. Thirty (30) seconds is the recommended level.
Sampling period: this is the interval at which the graph in the Activity pane is refreshed. The recommended period is 60 seconds to minimize overhead on WFS.
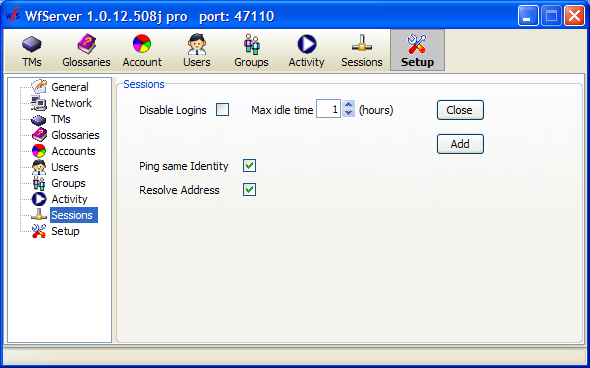
Disable logins: If you want to shut down the server, you may perhaps want to first block any new session from being opened. This checkbox, if checked, rejects any new login request, but keeps existing users logged on until they leave.
Max idle time: This is the maximum idle time until WFS terminates a user’s session (the maximum time without a ping or a request coming from a user).
Ping same identity: If two clients are logged with the same identity, this may indicate that one session crashed (or did not end with a proper end-of-session command), and the same user started a new session, with the first still opened. The server will ping both sessions to resolve the problem and know which of the two sessions is “orphaned” and should be ended. Each session has a unique session identifier that makes this operation possible.
Resolve address: Tries to get a clear domain name from a user’s DNS information.
| 06:08 |  |
| 06:19 | 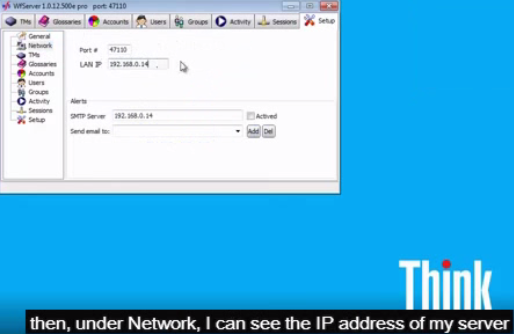 |
| 06:40 | 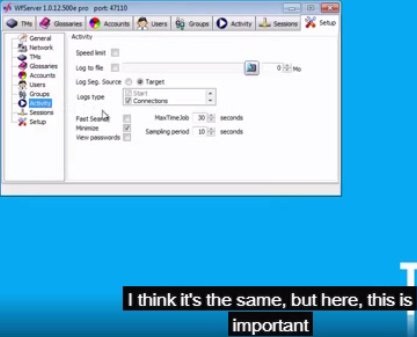 |
| 06:51 | 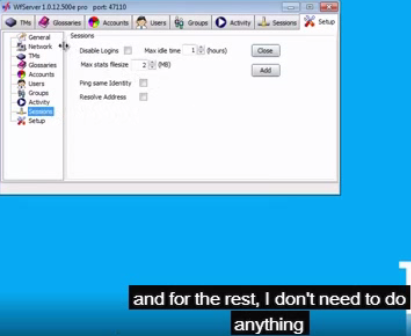 |
| 06:59 |  |