 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| English |
MetaTexis for Word Manual
 |
|---|
| E. | Quality Control | |
|---|---|---|
| BG | CA | CS | DA | DE | EL | ES | FI | FR | HR | HU | IS | IT | NL | NO | PL | PTp | RO | SB | SI | SW | WL | ||
| AF | AR | EO | FL | HE | IN | JA | KO | PTb | RU | TH | TR | ZHs | ZHt |
Quality control is an important aspect of any translation. MetaTexis has several functions that can help to improve the translation quality.
Of course, MetaTexis cannot check the stylistic quality of a translation. And, MetaTexis cannot check whether the content and the meaning of the source text were properly translated. This is the translator's task.
However, MetaTexis includes several powerful functions to check the formal quality of a translation. They are explained in detail in the next sections.
The most important quality check functions are the two go-to-functions in the Navigation sub-menu: Go to next translation unit to be revised, and Go to previous translation unit to be revised.
When one of these functions is executed, starting at the cursor position, each translation unit in the active document is checked to see whether it meets the quality requirements specified. While searching each area of the document is checked: main area, headers, footers, footnotes, endnotes, text boxes, and comments (if you have chosen to translate the comments). This means that if the search function runs through the whole document without stopping at any TU, you can be sure that the formal requirements specified are fulfilled in the whole document. If this is the case, a dialog box is shown informing you that no TU not meeting the formal requirements specified was found. You can then concentrate on the content and the stylistic aspects of the translation.
The go-to-function displays a TU if...
· It does not contain a translation
· It contains unedited results from a TM or TDB search
· It contains a watch list item (if the watch list is active)
· The number of words in the translation relative to the number of words in the source segment is lower/higher than the lower/upper limit specified (if the relevant function is active)
· The number of characters in the translation relative to the number of characters in the source segment is lower/higher than the lower/upper limit specified (if the relevant function is active)
· The number of numbers in the translation relative to the number of numbers in the source segment is lower/higher than the lower/upper limit specified (if the relevant function is active)
Whereas the watch list is a part of the Document options, the other quality check functions can be accessed via the General options dialog box. This may seem to be an inconsistency, but it is not. The watch list is closely related to the content of a document. Therefore, the watch list has to be saved in the document and cannot be viewed as "general".
On the other hand, the other quality check functions check purely formal aspects which, in principle, can be applied to every document (although to apply them can make more or less sense in certain cases).
All these features are explained in more detail below.
The watch list is a powerful means to check the quality of a translation. If the watch list is active, every TU is checked for watch list items. And when a watch list item is found you get a warning (or the search function displays the TU concerned).
You can activate the watch list function in the Document options dialog box. The first tab, Miscellaneous, contains the Watch list frame:
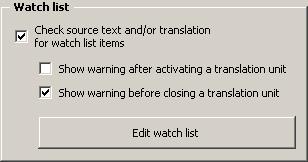
If you activate the Check source text and/or translation for watch list items check box, all TUs will be checked for watch list items.
You can also choose when to check the TU: after opening it and/or before closing it. If you deactivate both options, the watch list check will only be executed when you search for TUs to be revised, or when you start the quality check function manually, or when you check the whole document for watch list items (all functions are available in the Navigation sub-menu).
When you activate the watch list when the watch list is still empty, you are asked whether you want to edit the watch list. If you choose not to edit it, the watch list will be deactivated again.
Note: The number of watch list entries is limited to 1000 entries.
When you choose to edit the watch list, or when you click on the Edit watch list button, or when you click on the MetaTexis | Navigation | Edit watch list menu command, the following dialog box will appear:
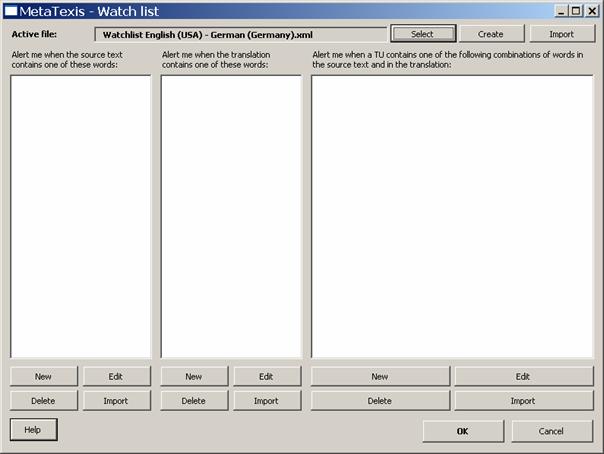
In the top margin of the dialog the active watch list file is displayed. When you activate the watch list feature for the first time, a new watch list file for the current language combination will automatically be created and saved in the standard watch list directory call "Watchlists" (located in the MetaTexis program directory). When you activate the watch list feature for another document, and a watch list file with the current language combination is already available, it will automatically be loaded.
Of course, you can also select another watch list, or create a new one by clicking the button Select or Create. By clicking the button Import you can import another watch list file into the active file.
Note: The watch list file has the XML format. You can easily edit it with other xml editors (like Word 2003) or watch it in the Internet Explorer. However, it is recommended to only edit it via the watch list dialog of MetaTexis to avoid inconsistencies.
The watch list consists of three different lists:
· Words in source text:
A warning is shown if the source text contains one or more of the words in this list.
· Words in translation:
A warning is shown if the translation contains one or more of the words in this list.
· Combination of words in source text and translation:
A warning is shown if the source text and the translation contain one or more of the combination of words in this list. The following logical combinations are possible:
|
(1) |
|
WordInSource |
NOT |
WordInTrans |
|
(2) |
NOT |
WordInSource |
|
WordInTrans |
|
(3) |
|
WordInSource |
|
WordInTrans |
|
(4) |
NOT |
WordInSource |
NOT |
WordInTrans |
Case (1) is the most common one: If the source text includes the WordInSource, a warning will be shown if the translation does NOT include the WordInTrans. Through this you can make sure that any terminology in the source text is translated consistently.
Case (2) can be used to detect misleading use of terminology. A warning will be shown if the translation includes the WordInTrans and the source text does not include the WordInSource.
Case (3) is another way to detect misleading use of terminology. A warning will be shown if the source text includes the WordInSource and if the translation contains the WordInTrans. The WordInTrans would be a wrong translation of the WordInSource, for example.
Case (4) is logically possible, but does not make sense in the most cases.
Below each list there are four buttons: Edit, New, Delete, Import. These buttons are explained below.
To add a new item to the Words in source text or Words in translation lists:
Click on the New button. The Edit watch list item dialog box will be displayed:
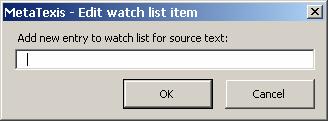
Enter a new word or phrase in the text box.
Click on OK to save and close the dialog box.
To add a new item to the Combination of words in source text and translation list:
33. Click on the New button. The Edit watch list item dialog box will be displayed:
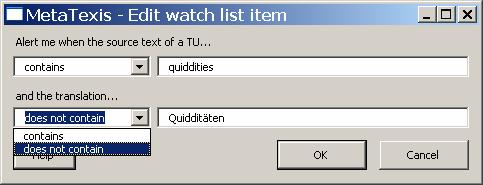
34. Enter two words or phrases: one for the source text and one for the translation.
35. Decide the logical condition for each word. In each case you can choose between "contains" and "does not contain" so that you have four possibilities to combine the two words. In this example you see the most common one: You will get a warning when the source text contains the word "quiddities" and the translation does not contain the word "Quidditäten".
36. To save and close the dialog box click on the OK button. After you have entered this item the watch list looks like this:
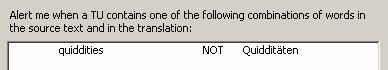
To edit a watch list entry:
37. Select the watch list entry to be edited.
38. Click on the relevant Edit button.
39. Edit the settings in the Edit watch list item dialog box shown.
40. Click on the OK button to save and close the dialog box.
To delete a watch list entry:
41. Select the watch list entry to be deleted.
42. Click on the relevant Delete button.
43. Confirm the deletion.
To import watch list items from a document into the Words in source text or Words in translation lists:
44. Click on the relevant Import button. The Import list dialog box will be displayed (for a complete image see "Import List Dialog Box" on page 2).
45. In the Options frame choose between Import words and Import lines.

If you choose to import words, each word will be imported as one watch list item. If you choose to import lines, each line will be imported as one watch list item.
46. Click on the Import button to import the watch list items and close the dialog box.
To import watch list items from a document into the Combination of words in source text and translation list:
47. Click on the relevant Import button. The Import list dialog box will be displayed (for a complete image see "Import List Dialog Box" on page 2).
48. In the Options frame enter the appropriate settings for the field separator and the content delimiter.
According to your settings the first two fields of one paragraph are imported as one watch list item. If one field is empty, it is excluded from the list.
49. Click on the Import button to import the watch list items and close the dialog box. When you import pairs of word into the list of word combinations, the pairs will be imported in this way: source text contains the first word, translation does not contain the second word. That is, you will be alarmed, when the word is found in the source text, and the translation is not found in the translation.
MetaTexis offers functions to check several formal aspects of a translation: number of words, number of characters, number of numbers, spell checking.
The formal quality checking options can be accessed via the General options dialog box:

If the Check formal quality of translation units check box is checked, MetaTexis checks the formal quality of the translations compared to the source text.
If neither the After activating check box, nor the Before closing are checked, the quality checks will only be performed when you execute a Go-to-command (see "Go to Functions" on page 2).
If you check the check box Warn me when the number of words in the translation is..., the number of words will be checked according to the settings made below. You can set and activate a lower tolerance limit and an upper tolerance limit. The default values are 50% for the lower limit and 200% for the upper limit. This leaves plenty of room for differences between languages as regards to the number of words used.
However, even if the translation is beyond theses limits, there is no guarantee that the translation is wrong - and vice versa! Please keep always in mind that you are the one to do the final checking!
If you check the Warn me when the number of characters in the translation is... check box, the number of characters will be checked according to the settings made below. You can set and activate a lower tolerance limit and an upper tolerance limit. The default values are 100% for the lower limit and 100% for the upper limit.
The default values may seem to make no sense as they do not leave any room for a difference. However, this function does make sense under very special circumstances, namely when there is the formal requirement that the number of characters in the translation must not be higher/lower then the number of characters in the source text. This can be the case in software localization projects.
If you check the Warn me when the number of numbers is not equal check box, the number of numbers is checked.
This function can be helpful when the text contains many numbers (which are not translated using words).
This function is not a crucial one, because Microsoft Word includes a built-in spell checker, which checks the spelling automatically. However, in some cases it can be useful to activate the Execute spell checking for translation unit check box:
· When the computer is slow and the automatic spell checker is not active for speed reasons
· When the active document contains too many spelling mistakes so that it is automatically de-activated by Microsoft Word itself
· When you want to make sure that the spelling is okay directly after editing a TU.